The StringList is a powerful data structure in Java that provides a dynamic collection of strings. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various capabilities of StringList and how to effectively use it in your Java code.
Introduction to StringList§
The StringList interface extends the List interface and inherits all the common operations from it. Some key benefits of using a StringList over a regular List or array include:
- Resizable collection specifically for strings
- Flexible insertion and removal of elements
- Powerful search and sorting capabilities
- Easy conversion to/from array
To create a StringList in Java:
1List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<>();
javaThe most common implementation is the ArrayList class. Let’s look at the key aspects of using a StringList in detail.
Creating and Initializing a StringList§
There are a few different ways to create and initialize a StringList in Java:
Using the Default Constructor§
1List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<>(); //empty list
javaInitializing with an Array of Strings§
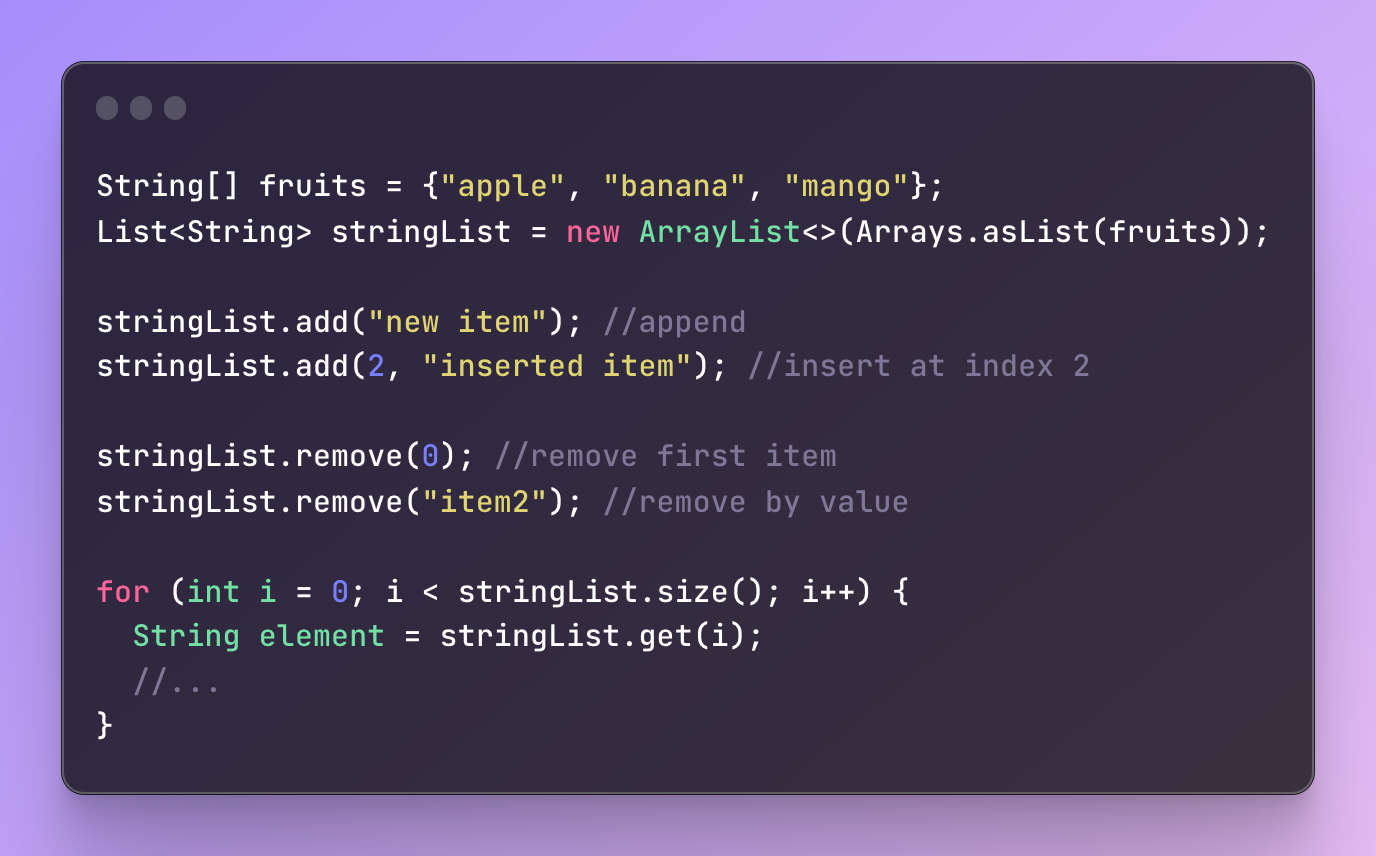
1String[] fruits = {"apple", "banana", "mango"};
2List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(fruits));
javaAdding Elements Dynamically§
1List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<>();
2stringList.add("item1");
3stringList.add("item2");
javaElements can be added at any time using the add() method.
Accessing and Modifying Elements§
The core operations on a StringList include:
Get Element by Index§
1String item = stringList.get(0); //first item
javaRetrieve First and Last Elements§
1String first = stringList.get(0);
2String last = stringList.get(stringList.size() - 1);
javaAdd Elements at End or Specific Index§
1stringList.add("new item"); //append
2stringList.add(2, "inserted item"); //insert at index 2
javaRemove Elements by Index or Value§
1stringList.remove(0); //remove first item
2stringList.remove("item2"); //remove by value
javaIterating through a StringList§
We can loop through the elements in a StringList using:
For Loop§
1for (int i = 0; i < stringList.size(); i++) {
2 String element = stringList.get(i);
3 //...
4}
javaEnhanced For Loop§
1for (String element : stringList) {
2 //...
3}
javaIterator§
1Iterator<String> it = stringList.iterator();
2while(it.hasNext()) {
3 String element = it.next();
4 //...
5}
javaSearching and Sorting§
StringList provides handy methods for searching and sorting:
Searching for an Element§
1int index = stringList.indexOf("item"); //linear search
javaSorting Elements§
1Collections.sort(stringList); //ascending sort
2Collections.sort(stringList, Comparator.reverseOrder()); //descending sort
javaFor a large sorted StringList, use Binary Search for efficiency.
Converting between StringList and Array§
1String[] array = stringList.toArray(new String[0]); //StringList to Array
2
3List<String> list = Arrays.asList(stringArray); //Array to StringList
javaStringList in Java 8 and Higher§
Some useful improvements in Java 8+:
| Feature | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Stream API | Enables functional-style operations on StringList | stringList.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("a")).count() |
| forEach() method | Iterate through elements | stringList.forEach(System.out::println) |
| removeIf() method | Remove elements by condition | stringList.removeIf(s -> s.length() < 5) |
| Collectors | Easily convert between collection types | Set<String> set = stringList.stream().collect(Collectors.toSet()); |
| joining() method | Join string elements | String joined = stringList.stream().collect(Collectors.joining(", ")) |
| Text blocks | Multiline string literals | String html = """ <html> <body> <p>Hello World</p> </body> </html> """; |
Conclusion§
The StringList is a very useful data structure in Java for managing collections of strings. With its flexible design and powerful methods, StringList enables easy string manipulation. This guide covered the key aspects of using StringList effectively in your code.